Channels
Special Offers & Promotions
Renishaw plc
Products
Contact Renishaw plc
All articles from Renishaw plc
Renishaw introduces the world's first Raman system with remote probes capable of focus-tracking
May 17, 2021
Live Webinar on Pharmaceutical Analysis using Raman Imaging on Thursday 27th September at 3:00 pm (UK)
Sep 5, 2018
Renishaw's inVia Confocal Raman microscope is Used to Study Blood Stored in Plastic Blood Bags
Jul 21, 2016
Media Partners
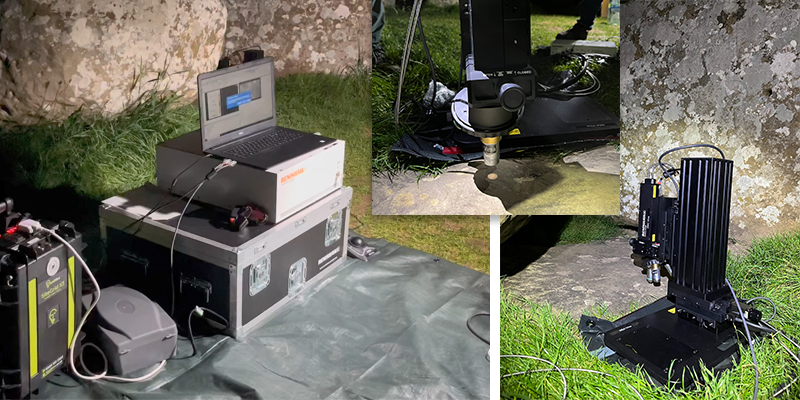
 In the quest to unravel the mysteries of Stonehenge, Renishaw had the privilege to assist in analysing the Altar Stone in situ using a Renishaw Virsa™ Raman analyser. The Altar Stone is unusual and differs in appearance when compared to the other main bluestones of Stonehenge. The aim was to use Raman spectroscopy and minerology to understand the provenance of the stone. Raman spectroscopy is ideal for this analysis as it is sensitive to the chemical and mineralogical composition of geological samples...
In the quest to unravel the mysteries of Stonehenge, Renishaw had the privilege to assist in analysing the Altar Stone in situ using a Renishaw Virsa™ Raman analyser. The Altar Stone is unusual and differs in appearance when compared to the other main bluestones of Stonehenge. The aim was to use Raman spectroscopy and minerology to understand the provenance of the stone. Raman spectroscopy is ideal for this analysis as it is sensitive to the chemical and mineralogical composition of geological samples... Renishaw is pleased to introduce fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) functionality to its inVia™ confocal Raman microscope. In partnership with Becker & Hickl GmbH, the pioneers in time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC), the system combines both Raman and FLIM in a single instrument. This integration can overlay both FLIM and Raman images with pixel-to-pixel correlation, thus increasing understanding of samples across a range of applications...
Renishaw is pleased to introduce fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (FLIM) functionality to its inVia™ confocal Raman microscope. In partnership with Becker & Hickl GmbH, the pioneers in time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC), the system combines both Raman and FLIM in a single instrument. This integration can overlay both FLIM and Raman images with pixel-to-pixel correlation, thus increasing understanding of samples across a range of applications...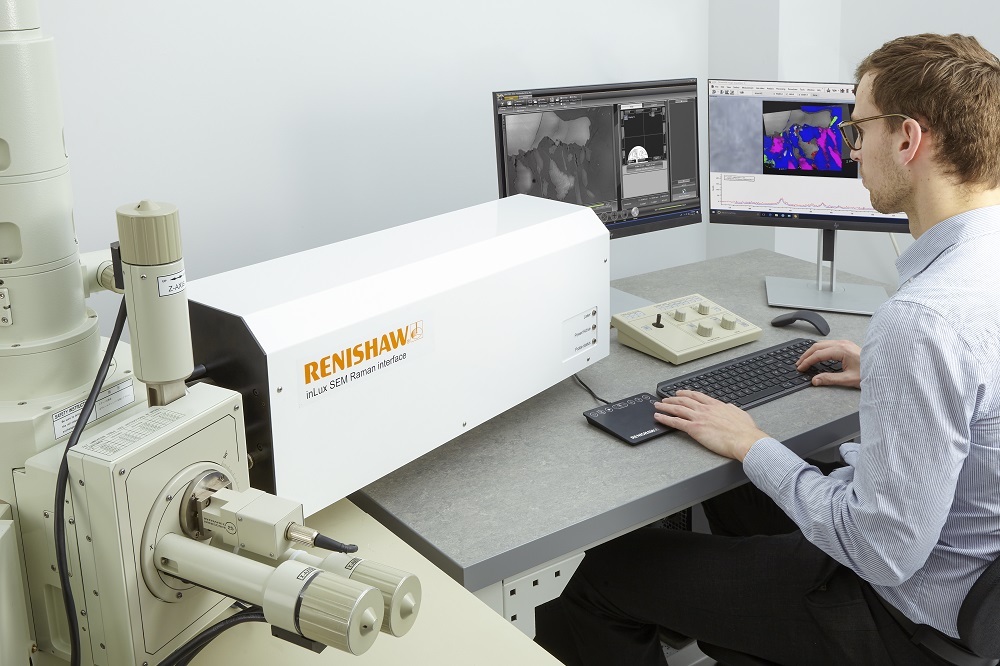 Renishaw, the pioneers in combining Raman spectroscopy with scanning electron microscopes (SEMs), have launched their latest product, the inLux SEM Raman interface. Adding the inLux interface to your SEM enables in situ Raman spectroscopy which provides highly specific chemical and structural characterisation to complement your SEM information. The inLux interface is compatible with SEMs from all major manufacturers and can be easily added to new and existing SEMs on site...
Renishaw, the pioneers in combining Raman spectroscopy with scanning electron microscopes (SEMs), have launched their latest product, the inLux SEM Raman interface. Adding the inLux interface to your SEM enables in situ Raman spectroscopy which provides highly specific chemical and structural characterisation to complement your SEM information. The inLux interface is compatible with SEMs from all major manufacturers and can be easily added to new and existing SEMs on site...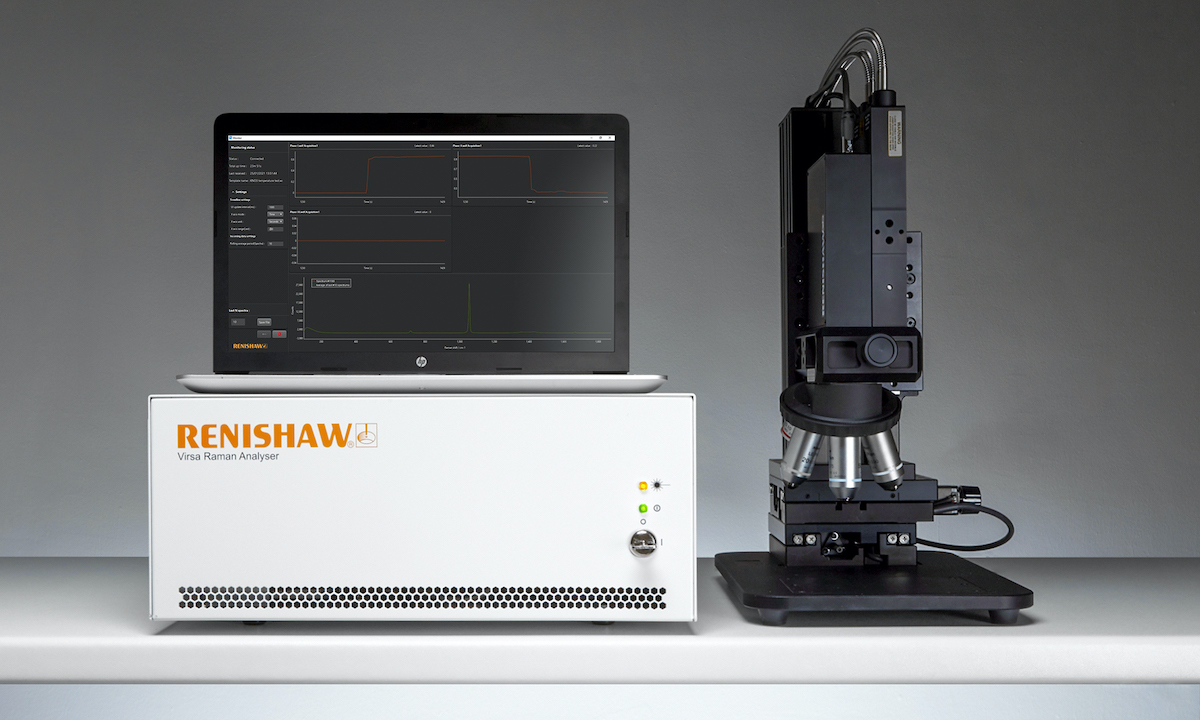 Renishaw's latest version of its Virsa™ Raman analyser, with new WiRE™ 5.5 software, enables its users to analyse samples away from the confines of the laboratory microscope, using remote fibre-optic probes. Its features expand the use of Raman spectroscopy to new samples, applications, and environments. The new Virsa system has LiveTrack™ focus-tracking technology and the new Monitor™ software module....
Renishaw's latest version of its Virsa™ Raman analyser, with new WiRE™ 5.5 software, enables its users to analyse samples away from the confines of the laboratory microscope, using remote fibre-optic probes. Its features expand the use of Raman spectroscopy to new samples, applications, and environments. The new Virsa system has LiveTrack™ focus-tracking technology and the new Monitor™ software module.... Renishaw has introduced the Particle Analysis software module for its inVia™ confocal Raman microscope. The module automates the inVia microscope so that it can identify particles on images and then chemically analyse them using Raman spectroscopy. Renishaw's inVia Raman system has a high-quality microscope that is ideal for producing optical images of particles on surfaces....
Renishaw has introduced the Particle Analysis software module for its inVia™ confocal Raman microscope. The module automates the inVia microscope so that it can identify particles on images and then chemically analyse them using Raman spectroscopy. Renishaw's inVia Raman system has a high-quality microscope that is ideal for producing optical images of particles on surfaces.... Coconut water has seen a recent boom in popularity. It is a very lucrative market, with London, England, being the biggest consumer of coconut water in the world (per head). There are at least 40 brands of coconut water in the United Kingdom alone and it can cost up to £4 per litre. With only five countries in the world supplying the majority of coconut water to the West, this surge...
Coconut water has seen a recent boom in popularity. It is a very lucrative market, with London, England, being the biggest consumer of coconut water in the world (per head). There are at least 40 brands of coconut water in the United Kingdom alone and it can cost up to £4 per litre. With only five countries in the world supplying the majority of coconut water to the West, this surge... Could rubber and plastic from tyres, washing into rivers and streams, be contributing to pollution in waste water? A group of scientists from Denmark are using a system from Renishaw to find out. Microplastics are small, hard-to-spot, particles that make their way—from products and packaging—into the environment and cause significant pollution. The Danish Technological Institute (DTI, Aarhus, Denmark) is using a Renishaw Raman spectroscopy system to...
Could rubber and plastic from tyres, washing into rivers and streams, be contributing to pollution in waste water? A group of scientists from Denmark are using a system from Renishaw to find out. Microplastics are small, hard-to-spot, particles that make their way—from products and packaging—into the environment and cause significant pollution. The Danish Technological Institute (DTI, Aarhus, Denmark) is using a Renishaw Raman spectroscopy system to... Renishaw inVia™ microscope user, Prof. Carlos A. Carrero, heads a group that is developing advanced catalysts for the conversion of hydrocarbons into more valuable products at the Department of Chemical Engineering, Auburn University, USA. The Carrero group undertakes fundamental studies to improve and develop more efficient and sustainable catalytic processes. They aim to develop the best catalysts using in situ / operando Raman spectroscopy to gather molecular, structural, and mechanistic insights....
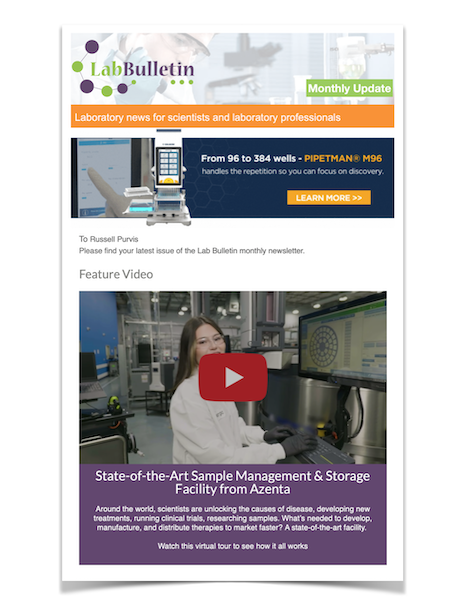
Renishaw inVia™ microscope user, Prof. Carlos A. Carrero, heads a group that is developing advanced catalysts for the conversion of hydrocarbons into more valuable products at the Department of Chemical Engineering, Auburn University, USA. The Carrero group undertakes fundamental studies to improve and develop more efficient and sustainable catalytic processes. They aim to develop the best catalysts using in situ / operando Raman spectroscopy to gather molecular, structural, and mechanistic insights....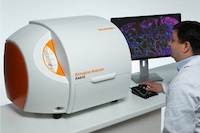 The new Renishaw RA816 Biological Analyser is a compact benchtop Raman imaging system, designed for biological and clinical research. This easy-to-use instrument enables the rapid collection of detailed information from a range of biological samples, including tissue and biofluids. Detailed biochemical information is revealed from biological samples. The Renishaw RA816 Biological Analyser enables biologists and clinicians to...
The new Renishaw RA816 Biological Analyser is a compact benchtop Raman imaging system, designed for biological and clinical research. This easy-to-use instrument enables the rapid collection of detailed information from a range of biological samples, including tissue and biofluids. Detailed biochemical information is revealed from biological samples. The Renishaw RA816 Biological Analyser enables biologists and clinicians to... Renishaw is delighted to have its RA802 Pharmaceutical Analyser shortlisted for a 2018 CPhI Pharma Award. The CPhI Pharma Awards, which are now in their 15th year, provide recognition to pharmaceutical companies that turn inspiration into innovation. They celebrate thinkers and creators breaking new ground in the industry and strongly advocate companies that are committed to driving the industry forward...
Renishaw is delighted to have its RA802 Pharmaceutical Analyser shortlisted for a 2018 CPhI Pharma Award. The CPhI Pharma Awards, which are now in their 15th year, provide recognition to pharmaceutical companies that turn inspiration into innovation. They celebrate thinkers and creators breaking new ground in the industry and strongly advocate companies that are committed to driving the industry forward... Drug development has become increasingly difficult and understanding formulation design space and the interplay raw materials properties and processing parameters have on the final drug product have never been more important. The rise of computational methods for drug design has yielded increasingly complex molecules....
Drug development has become increasingly difficult and understanding formulation design space and the interplay raw materials properties and processing parameters have on the final drug product have never been more important. The rise of computational methods for drug design has yielded increasingly complex molecules....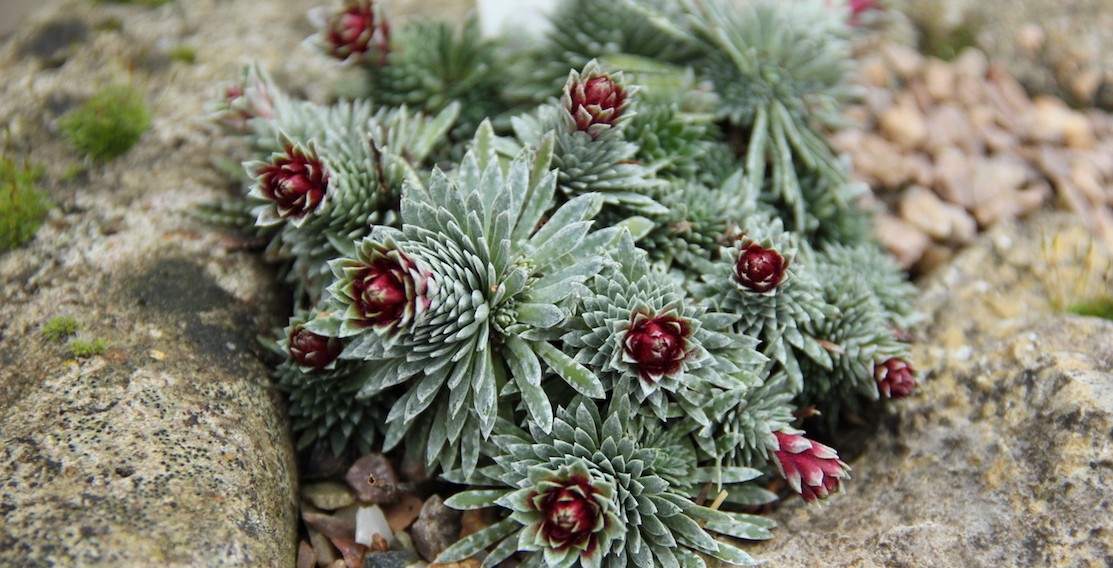 A team of scientists at the Sainsbury Laboratory Cambridge University (SLCU) have discovered a rare mineral in alpine plants. Vaterite, a form (polymorph) of calcium carbonate, holds enticing potential as a new material for industrial and medical applications. This is the first time that vaterite has been found in plants. The discovery of vaterite was made through a collaboration between SLCU and Cambridge University Botanic Garden....
A team of scientists at the Sainsbury Laboratory Cambridge University (SLCU) have discovered a rare mineral in alpine plants. Vaterite, a form (polymorph) of calcium carbonate, holds enticing potential as a new material for industrial and medical applications. This is the first time that vaterite has been found in plants. The discovery of vaterite was made through a collaboration between SLCU and Cambridge University Botanic Garden.... Plastics are used extensively in products and packaging. Unfortunately, these make their way into the environment and cause significant pollution, not only as bulk material but also as microplastics: small, hard-to-spot, particles. A Danish research institute is using a Raman spectroscopy system, from Renishaw, to help its clients understand and reduce the amount of microplastics in the environment...
Plastics are used extensively in products and packaging. Unfortunately, these make their way into the environment and cause significant pollution, not only as bulk material but also as microplastics: small, hard-to-spot, particles. A Danish research institute is using a Raman spectroscopy system, from Renishaw, to help its clients understand and reduce the amount of microplastics in the environment... Power generation is shifting from traditional to less predictable renewable sources.
Power generation is shifting from traditional to less predictable renewable sources.  They use a co-located SEM-Raman system from Renishaw to provide comprehensive in situ sample characterisation. Dr Guillaume Wille works in the Mineral Physicochemical and Textural Characterization Unit. In describing the analysis methods used at BRGM, Dr Wille said, “Numerous techniques are used, like infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy and microanalyses....
They use a co-located SEM-Raman system from Renishaw to provide comprehensive in situ sample characterisation. Dr Guillaume Wille works in the Mineral Physicochemical and Textural Characterization Unit. In describing the analysis methods used at BRGM, Dr Wille said, “Numerous techniques are used, like infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, electron microscopy and microanalyses.... It is famous for its museum which hosts a collection of more than 80,000 samples of rocks, fossils and minerals from all over Romania. Oana-Claudia Barbu and Daniel Bîrg?oanu are both PhD students and research assistants in the electron microscopy laboratory, known as MICROCOSMOS, where they study inorganic and mineral samples....
It is famous for its museum which hosts a collection of more than 80,000 samples of rocks, fossils and minerals from all over Romania. Oana-Claudia Barbu and Daniel Bîrg?oanu are both PhD students and research assistants in the electron microscopy laboratory, known as MICROCOSMOS, where they study inorganic and mineral samples....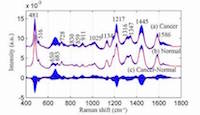 The proposed non-invasive blood test uses a combination of two techniques: surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and a new mathematical analysis technique called support vector machine (SVM). Together, these techniques produce an accuracy up to 98.1 percent; a far cry from the relative guesswork of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests...
The proposed non-invasive blood test uses a combination of two techniques: surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) and a new mathematical analysis technique called support vector machine (SVM). Together, these techniques produce an accuracy up to 98.1 percent; a far cry from the relative guesswork of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests... The research group of Professors Michael Blades and Robin Turner recently published this work in the Analyst. For this work the group collaborated with the Canadian Blood Services, using Raman microspectroscopy (RMS) to investigate the chemical changes that occur in red blood cells (RBC's), during storage in bags, which could eventually be used as a quality check prior to transfusion....
The research group of Professors Michael Blades and Robin Turner recently published this work in the Analyst. For this work the group collaborated with the Canadian Blood Services, using Raman microspectroscopy (RMS) to investigate the chemical changes that occur in red blood cells (RBC's), during storage in bags, which could eventually be used as a quality check prior to transfusion.... Building on the market-leading inVia Reflex, the inVia Qontor adds a new dimension to the performance and ease of use for which inVia is renowned. The inVia Qontor sees the addition of Renishaw's latest innovation, LiveTrack™ focus tracking technology, which enables users to analyse samples with uneven, curved or rough surfaces. Optimum focus is maintained in real time during data collection and white...
Building on the market-leading inVia Reflex, the inVia Qontor adds a new dimension to the performance and ease of use for which inVia is renowned. The inVia Qontor sees the addition of Renishaw's latest innovation, LiveTrack™ focus tracking technology, which enables users to analyse samples with uneven, curved or rough surfaces. Optimum focus is maintained in real time during data collection and white... Its ultimate goal is to develop a universal technology that allows precise determination of the actual spread of a tumour in vivo. Currently surgeons cannot see the microscopic extent of the tumour during a procedure, which is essential information for tumor removal and avoiding excess tissue excision. Physician-scientist Dr. Moritz Kircher is working on a new generation of nanometer-sized imaging beacons. These allow...
Its ultimate goal is to develop a universal technology that allows precise determination of the actual spread of a tumour in vivo. Currently surgeons cannot see the microscopic extent of the tumour during a procedure, which is essential information for tumor removal and avoiding excess tissue excision. Physician-scientist Dr. Moritz Kircher is working on a new generation of nanometer-sized imaging beacons. These allow... Within the Department, the Maruyama-Chiashi Laboratory focuses its research on the synthesis and analysis of carbon nanotubes (CNT), graphene and other nano-materials. They study applications related to the development of energy related devices, such as solar cells. The laboratory uses scanning Raman spectroscopy as an important tool for the investigation of the synthesized materials and their structure...
Within the Department, the Maruyama-Chiashi Laboratory focuses its research on the synthesis and analysis of carbon nanotubes (CNT), graphene and other nano-materials. They study applications related to the development of energy related devices, such as solar cells. The laboratory uses scanning Raman spectroscopy as an important tool for the investigation of the synthesized materials and their structure... It will be held, for the very first time, at Renishaw's New Mills headquarters in Gloucestershire. This one-day conference will bring together Raman users and experts from a diverse range of applications. Prominent scientists will present their current research involving Raman spectroscopy and attendees will be able to see Renishaw's latest Raman technology, capabilities and software...
It will be held, for the very first time, at Renishaw's New Mills headquarters in Gloucestershire. This one-day conference will bring together Raman users and experts from a diverse range of applications. Prominent scientists will present their current research involving Raman spectroscopy and attendees will be able to see Renishaw's latest Raman technology, capabilities and software... Dr Collin Becker is a mechanical engineer at the US Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in Maryland, USA. His group studies materials for advanced lithium ion batteries and future-generation energy storage systems, such as sodium ion, magnesium ion and solid-state batteries. His research on lithium ion batteries focuses on developing high capacity anode materials to improve the overall energy density, rate of discharge and safety of...
Dr Collin Becker is a mechanical engineer at the US Army Research Laboratory (ARL) in Maryland, USA. His group studies materials for advanced lithium ion batteries and future-generation energy storage systems, such as sodium ion, magnesium ion and solid-state batteries. His research on lithium ion batteries focuses on developing high capacity anode materials to improve the overall energy density, rate of discharge and safety of...