Channels
Special Offers & Promotions
Researchers Develop COVID-19 Severity Screening Method Based on the Agilent Cary 630 FTIR Spectrometer
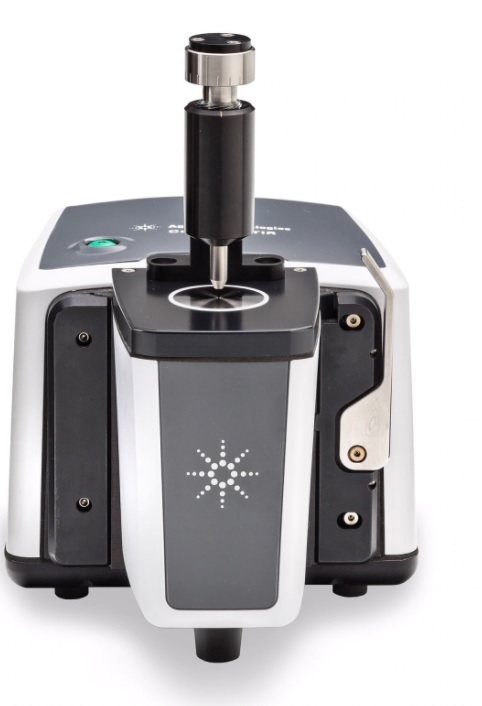

Agilent Technologies Inc. (NYSE: A) announces that researchers at the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay in India and the QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute in Australia have developed a rapid method for differentiating COVID-19-positive patients expected to show severe symptoms from those likely to experience only mild symptoms. The classification algorithm, published in the journal Analytical Chemistry, is based on infrared spectra of blood plasma, acquired on an Agilent Cary 630 FTIR Spectrometer.
The COVID-19 virus infected over 200 million people in 220 countries and territories in less than 18 months, overwhelming many healthcare systems 1. Resources such as ventilators and hospital beds remain in extremely high demand, and shortages risk the lives of severely ill patients. However, not all COVID-19 patients experience symptoms requiring intensive care. Early identification and prioritization (triage) of patients based on severity can help free up resources and improve patient outcomes 2. This research has the potential to provide significant support to healthcare workers facing critical resource decisions.
In the study, the researchers collected infrared spectra of blood plasma from 160 COVID-positive patients from Mumbai (130 as a training set for model development and 30 as a blind test set for model validation). The spectra, collected on a Cary 630 FTIR spectrometer equipped with a diamond-attenuated total reflectance (ATR) sampling module, revealed slight but observable differences between severe and non-severe COVID-19 patient samples.
Associate Professor Michelle Hill, head of QIMR Berghofer’s Precision and Systems Biomedicine Research Group, and one of the lead scientists of the study explained: “We found there were measurable differences in the infra-red spectra in the patients who became severely unwell. In particular, there were differences in two infra-red regions that correspond to sugar and phosphate chemical groups, as well as primary amines, which occur in specific types of proteins.”
Based on these differences, a multivariate statistical model was developed and tested.
Professor Sanjeeva Srivastava from the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay added: “We also found that having diabetes was a key predictor of becoming severely unwell in this group of patients, so we fed clinical parameters such as age, sex, diabetes mellitus, and hypertension into the algorithm. We then tested the algorithm on blood samples from a separate group of 30 patients from Mumbai and found it was 69.2% specific and 94.1% sensitive in predicting which patients would become severely ill.”
“However, it did result in more ‘false positives’ than predictions that were based solely on the clinical risk factors of age, sex, hypertension, and diabetes. We hope that with more testing, we can reduce these false positives”, Professor Srivastava further explained.
Andrew Hind, Associate Vice President of Research & Development for the Molecular Spectroscopy Division at Agilent, stated: “We are very excited about this study, and happily supported the researchers in their fight against COVID-19 by placing the Cary 630 FTIR spectrometer for this study. Their work highlights the potential of ATR-FTIR spectroscopy for COVID-19 and infectious disease research, and we will continue to support research in this field.”
The Agilent Cary 630 FTIR spectrometer is a versatile and reliable instrument used by researchers in high-impact studies worldwide. Its ultra-compact form, simplicity, and ease of use make it ideal for seamless deployment in many settings and scenarios. It is particularly well suited for use in infectious disease research and the investigation of biological samples. It can be paired with powerful multivariate statistical analysis to allow researchers to link spectral information with qualitative, macroscopic properties.
1. Worldometers: Coronavirus Update (Live) Cases and Deaths from COVID-19 Virus Pandemic. 2021
2. WHO Western Pacific Region: Algorithm for COVID-19 triage and referral
About Agilent Technologies
Agilent is a leader in life sciences, diagnostics, and applied chemical markets, delivering innovative technology solutions that provide trusted answers to researchers’ most challenging scientific questions. The company generated revenue of $5.34 billion in fiscal year 2020 and employs 16,400 people worldwide.
Media Partners