Channels
Special Offers & Promotions
Andor Technology plc
Products
Contact Andor Technology plc
All articles from Andor Technology plc
Deceptively Simple SCAPE 4D Microscope Brings Major Innovation to Live Cell and Whole Animal Imaging
Sep 19, 2017
Andor iXon 897 EMCCD camera discovers two undetected stars in well-mapped globular cluster
Jul 31, 2013
Bitplane Imaris Software to visualise effect of Neurobeachin on differentiation of synapses at Westf
Apr 5, 2012
Pioneering publication reports first ratiometric, single-protein red fluorescent pH sensor in live neurons
Jan 11, 2012
Andor deep-depletion CCD camera captures advance that could speed-up introduction of stem cell therapy
Oct 12, 2011
Sub 60-second identification of MRSA and other Hospital Acquired Infections demonstrated
Jan 14, 2011
Media Partners

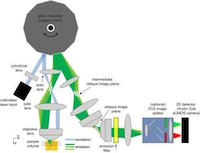 Advances in confocal, two-photon and light-sheet microscopy have rapidly advanced our understanding of cellular and subcellular structures and processes. However, live cell and whole animal imaging could be on the verge of even more breakthroughs following the publication in Nature Photonics of work by a team of Columbia University scientists....
Advances in confocal, two-photon and light-sheet microscopy have rapidly advanced our understanding of cellular and subcellular structures and processes. However, live cell and whole animal imaging could be on the verge of even more breakthroughs following the publication in Nature Photonics of work by a team of Columbia University scientists....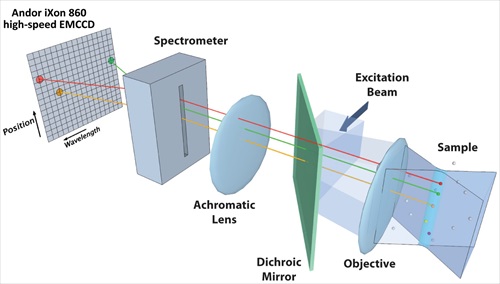 A unique hyperspectral microscope (HSM) designed specifically to visualise molecular-level protein-protein interactions in living cells has been unveiled recently by the University of Albuquerque. Designed around an Andor iXon 860 high-speed EMCCD detection system to record these profoundly challenging nanometer-scale events, the microscope delivers an unprecedented combination of speed, sensitivity and spectral detection. The novel design of the HSM provides acquisition rates of 27 fps over a 28 square micrometre field of view with each pixel collecting 128 spectral channels, allowing the determination of stoichiometry and dynamics of small oligomers unmeasurable by any other technique...
A unique hyperspectral microscope (HSM) designed specifically to visualise molecular-level protein-protein interactions in living cells has been unveiled recently by the University of Albuquerque. Designed around an Andor iXon 860 high-speed EMCCD detection system to record these profoundly challenging nanometer-scale events, the microscope delivers an unprecedented combination of speed, sensitivity and spectral detection. The novel design of the HSM provides acquisition rates of 27 fps over a 28 square micrometre field of view with each pixel collecting 128 spectral channels, allowing the determination of stoichiometry and dynamics of small oligomers unmeasurable by any other technique...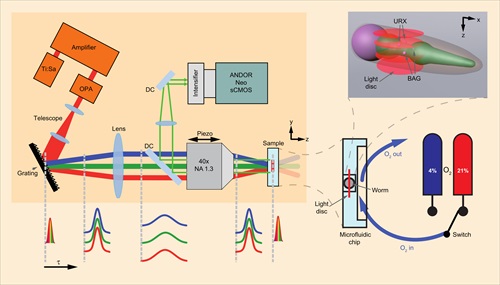
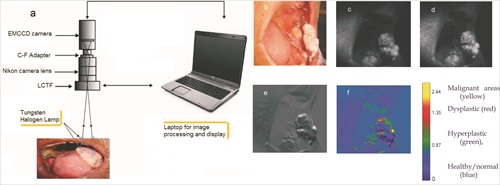 A team of Indian cancer researchers led by Dr Narayanan Subhash has developed a simple, non-invasive spectral imaging system that holds out the possibility of rapid, inexpensive mass screening for oral cancers in dental and clinical settings. Even in the hands of non-clinical staff, it is capable of real-time discrimination of healthy oral tissue from pre-malignant and malignant tissues with accuracy comparable to the gold standard histopathology of a biopsy sample....
A team of Indian cancer researchers led by Dr Narayanan Subhash has developed a simple, non-invasive spectral imaging system that holds out the possibility of rapid, inexpensive mass screening for oral cancers in dental and clinical settings. Even in the hands of non-clinical staff, it is capable of real-time discrimination of healthy oral tissue from pre-malignant and malignant tissues with accuracy comparable to the gold standard histopathology of a biopsy sample....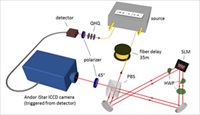
 The location of the site where autophagosomal membranes are created within the cell has been the subject of two competing models for many years. Now, a group of researchers from Osaka University led by Prof. Maho Hamasaki has located the origin of autophagosomes within the cell and shown that neither model is correct. Writing in Nature, they show that autophagosomes form at the contact site of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with mitochondria. Live cell imaging studies, using an Andor Revolution XD spinning disk confocal microscope equipped with three Andor iXon 3 EMCCD cameras, captured previously hidden detail...
The location of the site where autophagosomal membranes are created within the cell has been the subject of two competing models for many years. Now, a group of researchers from Osaka University led by Prof. Maho Hamasaki has located the origin of autophagosomes within the cell and shown that neither model is correct. Writing in Nature, they show that autophagosomes form at the contact site of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with mitochondria. Live cell imaging studies, using an Andor Revolution XD spinning disk confocal microscope equipped with three Andor iXon 3 EMCCD cameras, captured previously hidden detail...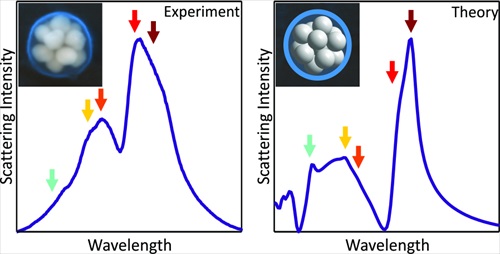 Recent advances in nanotechnology have created a novel breed of optically active materials fabricated from highly-structured two-dimensional arrays of noble metal nanoparticles. Now, a team from Rice University in Houston, Texas, has developed a method to manufacture stable, three-dimensional (3-D) nanoclusters that could be used to impart metamaterial optical properties into unstructured substrates such as liquids, glasses and plastics....
Recent advances in nanotechnology have created a novel breed of optically active materials fabricated from highly-structured two-dimensional arrays of noble metal nanoparticles. Now, a team from Rice University in Houston, Texas, has developed a method to manufacture stable, three-dimensional (3-D) nanoclusters that could be used to impart metamaterial optical properties into unstructured substrates such as liquids, glasses and plastics....
 Since the first demonstrations of Bose-Einstein condensation in 1995, ultra-cold matter has become a fertile and lively field of study. Research around the world is establishing a high level of understanding of the underlying physics for applications, such as inertial guidance systems, atomic clocks and quantum computing. Teams are also beginning to design and build compact, low-power instrumentation for handling ultra-cold atoms...
Since the first demonstrations of Bose-Einstein condensation in 1995, ultra-cold matter has become a fertile and lively field of study. Research around the world is establishing a high level of understanding of the underlying physics for applications, such as inertial guidance systems, atomic clocks and quantum computing. Teams are also beginning to design and build compact, low-power instrumentation for handling ultra-cold atoms... With the accelerating interest in seeking out Earth 2.0 exoplanets, the need for accurate star maps on which to base our searches only increases. However, an international team of scientists has found two previously undetected stars in a recently mapped globular cluster using the ultra-sensitive Andor iXon 897 Electron Multiplying CCD camera on the Danish 1.54m telescope at La Silla, Chile. This discovery raises the possibility that we can pinpoint more potential target planets that would be hospitable to life...
With the accelerating interest in seeking out Earth 2.0 exoplanets, the need for accurate star maps on which to base our searches only increases. However, an international team of scientists has found two previously undetected stars in a recently mapped globular cluster using the ultra-sensitive Andor iXon 897 Electron Multiplying CCD camera on the Danish 1.54m telescope at La Silla, Chile. This discovery raises the possibility that we can pinpoint more potential target planets that would be hospitable to life...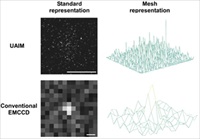
 As the worldwide race to discover Earth-like exoplanets accelerates, Andor's expertise in high-performance digital camera design and manufacture is proving crucial for many of the leading groups in the field. SuperWASP (Wide Angle Search for Planets) has proven to be one of the most successful projects, finding more than a third of all confirmed transiting planetary systems through its two telescopes, each equipped with eight Andor iKon-L cameras.
As the worldwide race to discover Earth-like exoplanets accelerates, Andor's expertise in high-performance digital camera design and manufacture is proving crucial for many of the leading groups in the field. SuperWASP (Wide Angle Search for Planets) has proven to be one of the most successful projects, finding more than a third of all confirmed transiting planetary systems through its two telescopes, each equipped with eight Andor iKon-L cameras.  In a recently published paper, a team from Saarland University's Biophysics and Cryotechnology department in Germany has demonstrated a powerful, Raman-scattering technique for monitoring and investigating cryopreserved samples. In particular, they confirmed unambiguously the detection of ice crystals in vitreous samples in situ at temperatures below -120°C....
In a recently published paper, a team from Saarland University's Biophysics and Cryotechnology department in Germany has demonstrated a powerful, Raman-scattering technique for monitoring and investigating cryopreserved samples. In particular, they confirmed unambiguously the detection of ice crystals in vitreous samples in situ at temperatures below -120°C....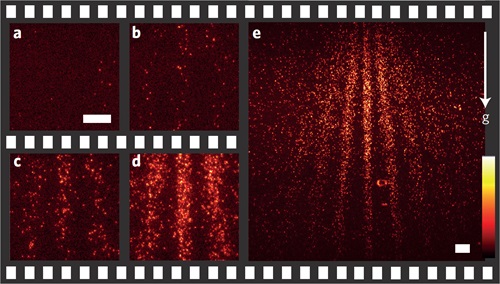 Described as the "most beautiful experiment in physics", Richard Feynman spoke of the double-slit experiment as 'the heart of quantum physics', emphasizing how the diffraction of individual particles at a grating is an unambiguous demonstration of wave-particle duality and contrary to classical physics. Matter-wave interference has been observed for almost 90 years, first for electrons, neutrons, atoms, and small molecules. The first single-electron/double-slit experiment to back-up Feynman's assertion that an individual electron itself can behave like a wave was reported by Tonomura's team in 1989....
Described as the "most beautiful experiment in physics", Richard Feynman spoke of the double-slit experiment as 'the heart of quantum physics', emphasizing how the diffraction of individual particles at a grating is an unambiguous demonstration of wave-particle duality and contrary to classical physics. Matter-wave interference has been observed for almost 90 years, first for electrons, neutrons, atoms, and small molecules. The first single-electron/double-slit experiment to back-up Feynman's assertion that an individual electron itself can behave like a wave was reported by Tonomura's team in 1989.... Laboratories in Europe and the USA have independently announced in the same issue of Nature Methods the development of new microscopes capable of imaging rapid biological processes in thick samples in unprecedented detail and ideally suited to the long-term study of live biological specimens...
Laboratories in Europe and the USA have independently announced in the same issue of Nature Methods the development of new microscopes capable of imaging rapid biological processes in thick samples in unprecedented detail and ideally suited to the long-term study of live biological specimens...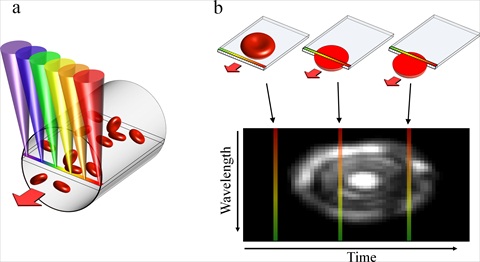 An Israeli team has demonstrated a non-invasive technique for imaging blood cells in vivo that could eliminate the need to extract blood from many patients. Powered by the Andor Newton Electron Multiplying EMCCD camera, their high-resolution Spectrally Encoded Flow Cytometry (SEFC) probe offers primary care physicians the capability to detect directly a wide range of common medical disorders, such as anaemia and bacterial infection, and potentially life threatening conditions, including sepsis, thrombosis and sickle cell crisis...
An Israeli team has demonstrated a non-invasive technique for imaging blood cells in vivo that could eliminate the need to extract blood from many patients. Powered by the Andor Newton Electron Multiplying EMCCD camera, their high-resolution Spectrally Encoded Flow Cytometry (SEFC) probe offers primary care physicians the capability to detect directly a wide range of common medical disorders, such as anaemia and bacterial infection, and potentially life threatening conditions, including sepsis, thrombosis and sickle cell crisis... One of the challenges facing neuroscience researchers is understanding how nerve cells contact each other to transmit information and which proteins and mechanisms control the formation and function of these synaptic contacts. Most excitatory synapses in the brain are built on actin-rich dendritic protrusions called spines and, as numerous psychiatric and neurological diseases are accompanied by alterations of spine numbers or size, the elucidation of mechanisms that regulate formation and plasticity of spinous synapses is vital...
One of the challenges facing neuroscience researchers is understanding how nerve cells contact each other to transmit information and which proteins and mechanisms control the formation and function of these synaptic contacts. Most excitatory synapses in the brain are built on actin-rich dendritic protrusions called spines and, as numerous psychiatric and neurological diseases are accompanied by alterations of spine numbers or size, the elucidation of mechanisms that regulate formation and plasticity of spinous synapses is vital... Malignant melanoma (MM), the most dangerous type of skin cancer, is caused mainly by intense episodes of UV exposure and originates in the pigment-producing melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis. Early detection and complete excision of the primary lesions is crucial for reducing melanoma-related deaths but current diagnostic practice is highly subjective. This leads to unnecessary surgical procedures, which are highly-invasive and expensive...
Malignant melanoma (MM), the most dangerous type of skin cancer, is caused mainly by intense episodes of UV exposure and originates in the pigment-producing melanocytes in the basal layer of the epidermis. Early detection and complete excision of the primary lesions is crucial for reducing melanoma-related deaths but current diagnostic practice is highly subjective. This leads to unnecessary surgical procedures, which are highly-invasive and expensive...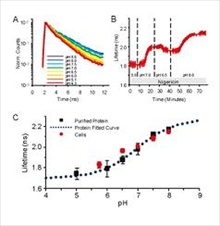 The importance that intracellular pH plays in cell biology is highlighted in a new paper published by the American Chemical Society. Written by a group of researchers from Harvard Medical School led by Professor Gary Yellen, it reports the engineering of the first ratiometric, single-protein red fluorescent sensor of pH, called pHRed, and its use to image intracellular pH in live neuronal cells...
The importance that intracellular pH plays in cell biology is highlighted in a new paper published by the American Chemical Society. Written by a group of researchers from Harvard Medical School led by Professor Gary Yellen, it reports the engineering of the first ratiometric, single-protein red fluorescent sensor of pH, called pHRed, and its use to image intracellular pH in live neuronal cells... If you can't tell your Bruichladdich from your Irn-Bru, or your Glenfiddich from your Glenmorangie, help is at hand from the physics department at St Andrews University. Praveen Ashok, Kishan Dholakia and Bavishna Praveen of the optical manipulation group have developed a microfluidic device that can not only detect counterfeit whisky samples but also characterise genuine samples by brand, age and, even, cask...
If you can't tell your Bruichladdich from your Irn-Bru, or your Glenfiddich from your Glenmorangie, help is at hand from the physics department at St Andrews University. Praveen Ashok, Kishan Dholakia and Bavishna Praveen of the optical manipulation group have developed a microfluidic device that can not only detect counterfeit whisky samples but also characterise genuine samples by brand, age and, even, cask...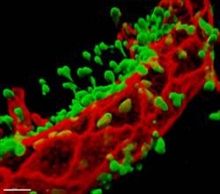 The migration of neutrophils from the vascular lumen into inflamed tissues is a crucial component of the normal immune response and a significant factor in the development of inflammatory pathologies, where inappropriate inflammation contributes to tissue damage and disease progression. A decisive step in this process is the passage of the blood neutrophils through the endothelial cells lining the lumen - transendothelial migration (TEM)...
The migration of neutrophils from the vascular lumen into inflamed tissues is a crucial component of the normal immune response and a significant factor in the development of inflammatory pathologies, where inappropriate inflammation contributes to tissue damage and disease progression. A decisive step in this process is the passage of the blood neutrophils through the endothelial cells lining the lumen - transendothelial migration (TEM)... Many medical researchers believe that stem cell therapy will revolutionise the treatment of human disease and may provide treatments for many currently incurable diseases. However, one problem still to be overcome is controlling the excessive proliferation of cells with unwanted phenotypes after transplantation to prevent tissue overgrowth and tumour formation...
Many medical researchers believe that stem cell therapy will revolutionise the treatment of human disease and may provide treatments for many currently incurable diseases. However, one problem still to be overcome is controlling the excessive proliferation of cells with unwanted phenotypes after transplantation to prevent tissue overgrowth and tumour formation... Andor iDus camera captures dramatic results that promise major advances for highly efficient solar energy photoelectric devices development, precise optical imaging and single molecule detection. Nanoscale antennas hold out the promise of higher resolution optical imaging of nano objects, including proteins and DNA molecules, and converting solar energy into electricity at very high efficiencies. Now, a team from the University of Illinois led by Nicholas Fang and Kimani Toussaint has demonstrated a 1,000-fold increase in the UV-Visible optical response of devices based on nanoantennas periodic arrays...
Andor iDus camera captures dramatic results that promise major advances for highly efficient solar energy photoelectric devices development, precise optical imaging and single molecule detection. Nanoscale antennas hold out the promise of higher resolution optical imaging of nano objects, including proteins and DNA molecules, and converting solar energy into electricity at very high efficiencies. Now, a team from the University of Illinois led by Nicholas Fang and Kimani Toussaint has demonstrated a 1,000-fold increase in the UV-Visible optical response of devices based on nanoantennas periodic arrays... Using the Andor Revolution XD Confocal Microscope for live cell studies, Prof. Puthenveedu has led an international team of researchers to elucidate how signalling receptors are recycled to the cell membrane. The discovery of the mechanism by which signalling receptors travel back to the surface of the cell after activation and internalisation opens up a new class of therapeutic targets...
Using the Andor Revolution XD Confocal Microscope for live cell studies, Prof. Puthenveedu has led an international team of researchers to elucidate how signalling receptors are recycled to the cell membrane. The discovery of the mechanism by which signalling receptors travel back to the surface of the cell after activation and internalisation opens up a new class of therapeutic targets...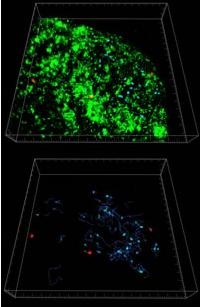 Dr Patricia Barral and her colleagues study the cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling lymphocyte activation and eventual fate. Knowledge of these processes is invaluable not only in increasing our understanding of the causes of cancer but also in the treatment and prevention of infectious and autoimmune diseases.
Dr Patricia Barral and her colleagues study the cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling lymphocyte activation and eventual fate. Knowledge of these processes is invaluable not only in increasing our understanding of the causes of cancer but also in the treatment and prevention of infectious and autoimmune diseases. At a time of rising levels of MRSA and other hospital acquired infections, Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) has been demonstrated to be a rapid and reliable technique for detection of life-threatening bacterial pathogen species that can be found in such medical environments. For the first time, scientists have used Chemometrics analysis of LIBS data in a blind test to successfully identify five pathogenic bacterial samples and differentiate between strains of a multiple-antibiotic-resistant species.
At a time of rising levels of MRSA and other hospital acquired infections, Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) has been demonstrated to be a rapid and reliable technique for detection of life-threatening bacterial pathogen species that can be found in such medical environments. For the first time, scientists have used Chemometrics analysis of LIBS data in a blind test to successfully identify five pathogenic bacterial samples and differentiate between strains of a multiple-antibiotic-resistant species.